- The physical construction of shock absorber bushings include a hardened steel back and PTFE on the inner lining.
- Bushings used in shock absorbers are specifically designed for linear applications.
- Shock absorber bushings help to cushion movement and vibration found in the vehicle suspension system.
Shock absorber bushing functionality
Shock absorbers help to improve vehicle handling and make the ride smoother for the occupants. As the vehicle moves over bumps in the road, the shocks work to keep all four tires firmly on the ground. They do this by absorbing the jolts and undulations in the road.
Composition of shock absorber bushings
Shock absorber bushings come in common forms – rubber and metal. Rubber bushings are at the top and bottom of the shock absorber and are used to attach the shock to the vehicle’s frame and control arm. These bushings are sometimes spherical plain bearings or rod ends in a rubber housing.
PTFE bushings are located on the interior nose of the shock and contact with the piston rod. The PTFE can be sintered to the inside or outside of the bushing, depending on the application. These bushings provide precise and quick movement against the rod resisting wear and friction. Long performance life is gained from the use of PTFE bushing in shock applications.
Shock Absorber Bushing Options
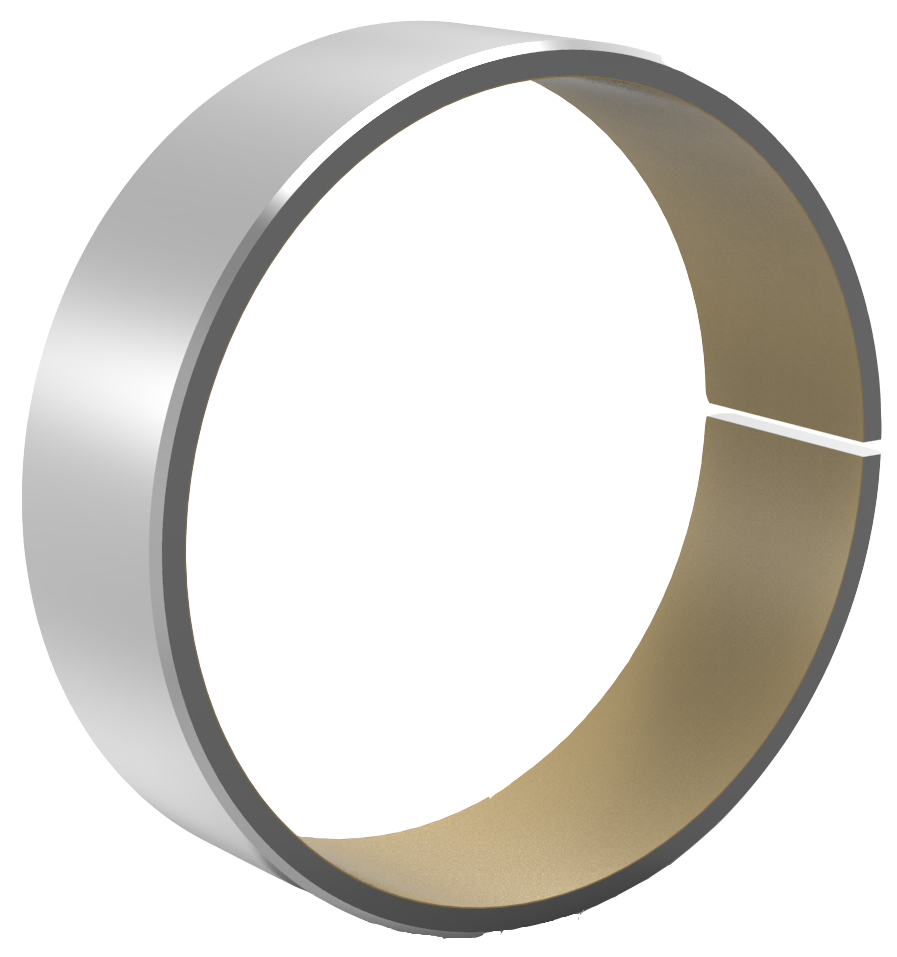
PTFE on Inner Ring PTFE on Exterior
What OEMs look for in shock absorber bushings
Original equipment manufacturers look for RoHS-compliant material that is optimized for wear and friction resistance in linear motion and reciprocating sliding applications. The bushing composition must also be highly precise to operate within close clearance fits and broad temperature extremes.
The bottom line
Shock absorber bushings are part of what makes driving enjoyable. They help to ensure a smooth ride and long shock absorber performance life.